Overview
Implement Logistic Regression Using IPython notebook
Logistic Regression without regularization
visualize the data
import modules numpy and matplotlib
# build in the pyplot into notebook
%matplotlib inline
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import the sample data from the files
fileName = 'ex2/data/ex2data1.txt'
cols = np.loadtxt(fileName, np.float, delimiter=',',usecols=(0,1,2),unpack=True)
X = cols[:-1].T
Y = cols[-1:].T
X = np.insert(X, 0, 1, axis=1) #axis = 1 means to insert the 1 before column index:0; it axis = 0, insert before the row index:0
posX = np.array([X[i] for i in xrange(len(X)) if Y[i][0]==1])
negX = np.array([X[i] for i in xrange(len(X)) if Y[i][0]==0])
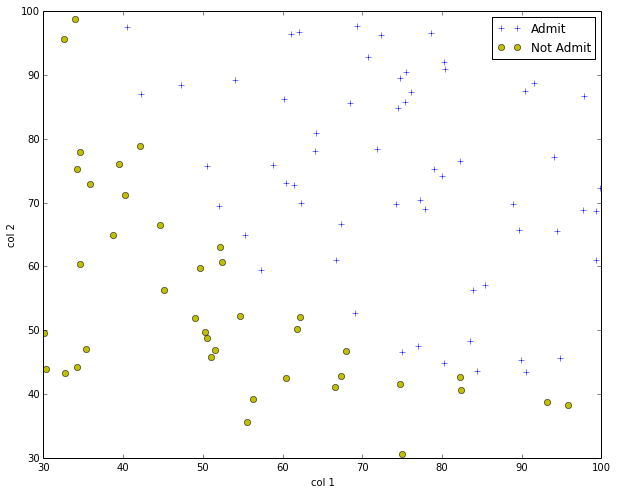
visulization the samples
def plotData(X, Y):
# filter to get positive and negative examples
plt.figure(figsize=(10,8)) # create a figure canvas
plt.plot(posX[:,1],posX[:,-1],'+',label='Admit')
plt.plot(negX[:,1],negX[:,-1],'yo',label='Not Admit')
plt.xlabel('col 1')
plt.ylabel('col 2')
plt.legend()
plotData(X,Y)
plt.show()
Use sigmoid function to separate the data
the activation function
\(g(x)=\frac{1}{1+e^{-z}}\)
其中 \(z = X \Theta\)
当\(z >= 0\)时, \(g(x) >= 0.5\)
当\(z < 0 \)时, \(g(x) < 0.5\)
the loss function
\(J(\theta) = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m}[-y^i log(h_{\theta}(x^i)) - (1 - y^i) log(1 - h_{\theta}(x^i))]\)
the gradient of the cost:
\(\frac{\partial J(\theta))}{\partial \theta_j} = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m}(h_{\theta}(x^i) - y^i)x_j^i\)
implementation using sigmoid function
# define the iteration = 400
iterations = 400
# define the init_theta = 0
init_theta = np.zeros((X.shape[1],1))
# import the module optimize from SciPy
from scipy import optimize
def f(z):
return 1.0/(1 + np.exp(-z))
def costFunction(theta, X, Y, mylambda=0.0):
theta = theta.reshape(-1,1)
Z = np.dot(X,theta)
T = f(Z)
result = np.sum(Y * np.log(T) + (1 - Y)*np.log(1-T)) * (-1) / len(X)
if np.isnan(result):
return np.inf
return result
def gradient(theta, X, Y):
theta = theta.reshape(-1,1)
#print theta, theta.shape
Z = np.dot(X, theta) # m*1
T = f(Z)
result = np.dot(X.T,T - Y) / len(X) # n * 1
return result.flatten()
costFunction(init_theta,X,Y)
0.69314718055994584
theta = init_theta
print theta.shape
result = optimize.minimize(costFunction,theta,args=(X,Y),method='BFGS',jac=gradient, options={'maxiter':400})
print result
(3, 1)
status: 0
success: True
njev: 30
nfev: 30
hess_inv: array([[ 3.07660923e+03, -2.46603141e+01, -2.46347979e+01],
[ -2.46603141e+01, 2.11901191e-01, 1.84691126e-01],
[ -2.46347979e+01, 1.84691126e-01, 2.12563326e-01]])
fun: 0.20349770158966385
x: array([-25.16136291, 0.20623191, 0.20147189])
message: ‘Optimization terminated successfully.’
jac: array([ 5.11757491e-08, 2.27330775e-06, 5.15598733e-06])
costFunction(result.x,X,Y)
0.20349770158966385
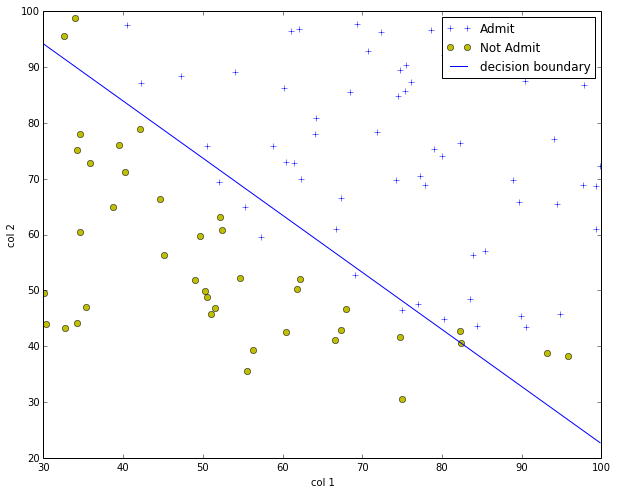
visualize the boundary
plotData(X,Y)
theta = result.x
boundary_x = np.array([np.min(X[:,1]),np.max(X[:,1])]) # x boundary
boundary_y = (boundary_x * theta[1] + theta[0]) * (-1.0)/theta[2]
plt.plot(boundary_x, boundary_y, 'b-',label='decision boundary')
plt.legend()
plt.show()
predict precision
def makePredict(theta, X):
return f(np.dot(X, theta.reshape(-1,1))) >=0.5
pos_count = float(np.sum(makePredict(theta, posX)))
neg_count = float(np.sum(np.invert(makePredict(theta,negX))))
print "Fraction of training samples correctly predicted: %f." % ((pos_count + neg_count) / (len(posX) + len(negX)))
Fraction of training samples correctly predicted: 0.890000.
logistic regression with regularization
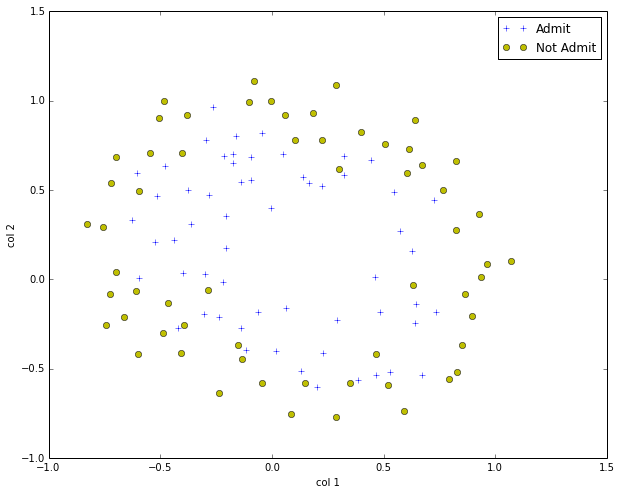
visualize the sample data
extract data from the txt file
fileName = 'ex2/data/ex2data2.txt'
cols = np.loadtxt(fileName, np.float, delimiter=',',usecols=(0,1,2),unpack=True)
X = cols[:-1].T
Y = cols[-1:].T
X = np.insert(X, 0, 1, axis=1) #axis = 1 means to insert the 1 before column index:0; it axis = 0, insert before the row index:0
posX = np.array([X[i] for i in xrange(len(X)) if Y[i][0]==1])
negX = np.array([X[i] for i in xrange(len(X)) if Y[i][0]==0])
plotData(X,Y)
map the features
def mapFeatures(col1, col2):
degree = 6
m = len(col1)
out = np.ones((m,1))
for i in xrange(1, degree+1):
for j in xrange(0, i+1):
term1 = col1 ** (i-j)
term2 = col2 ** j
term = (term1 * term2)
# print term.shape
term = term.reshape((m,1))
out = np.hstack((out,term))
return out
mappedX = mapFeatures(X[:,1],X[:,-1])
print mappedX
The output is:
[[ 1.00000000e+00 5.12670000e-02 6.99560000e-01 ..., 6.29470940e-04
8.58939846e-03 1.17205992e-01]
[ 1.00000000e+00 -9.27420000e-02 6.84940000e-01 ..., 1.89305413e-03
-1.39810280e-02 1.03255971e-01]
[ 1.00000000e+00 -2.13710000e-01 6.92250000e-01 ..., 1.04882142e-02
-3.39734512e-02 1.10046893e-01]
...,
[ 1.00000000e+00 -4.84450000e-01 9.99270000e-01 ..., 2.34007252e-01
-4.82684337e-01 9.95627986e-01]
[ 1.00000000e+00 -6.33640000e-03 9.99270000e-01 ..., 4.00328554e-05
-6.31330588e-03 9.95627986e-01]
[ 1.00000000e+00 6.32650000e-01 -3.06120000e-02 ..., 3.51474517e-07
-1.70067777e-08 8.22905998e-10]]
formula with regularization
\(J(\theta) = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m}[-y^i log(h_{\theta}(x^i)) - (1 - y^i) log(1 - h_{\theta}(x^i))] + \frac{\lambda}{2m} \sum_{j=1}^{m}\theta_j^2\)
the gradient of the cost:
\(\frac{\partial J(\theta))}{\partial \theta_0} = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m}(h_{\theta}(x^i) - y^i)x_0^i\) for \(j=0\)
\(\frac{\partial J(\theta))}{\partial \theta_j} = \frac{1}{m} \sum_{i=1}^{m}(h_{\theta}(x^i) - y^i)x_j^i + \frac{\lambda}{m} \theta_j\) for \(j=1,2,\cdots,n\)
implementation
def costFunctionWithReg(theta, X, Y, mylambda=0.0):
theta = theta.reshape(-1,1)
Z = np.dot(X,theta)
T = f(Z)
m = len(X)
result = np.sum(Y * np.log(T) + (1 - Y)*np.log(1-T)) * (-1) / len(X)
theta2 = theta[1:,:]
result = result + (mylambda / (2* m)) * np.dot(theta2.T,theta2)
if np.isnan(result):
return np.inf
return result
def gradientWithReg(theta, X, Y, mylambda = 0.0):
theta = theta.reshape(-1,1)
# print theta, theta.shape
Z = np.dot(X, theta) # m*1
T = f(Z)
m = len(X)
result = np.dot(X.T,T - Y) / len(X) # n * 1
theta[0] = 0
result = result + (mylambda / m) * theta
return result.flatten()
result = optimize.minimize(costFunctionWithReg, np.zeros((mappedX.shape[1],1)), args=(mappedX,Y,0.0), method='BFGS',
jac=gradientWithReg,options={'maxiter':500,'disp':True})
Now come to the result:
Warning: Maximum number of iterations has been exceeded.
Current function value: 0.238242
Iterations: 500
Function evaluations: 501
Gradient evaluations: 501
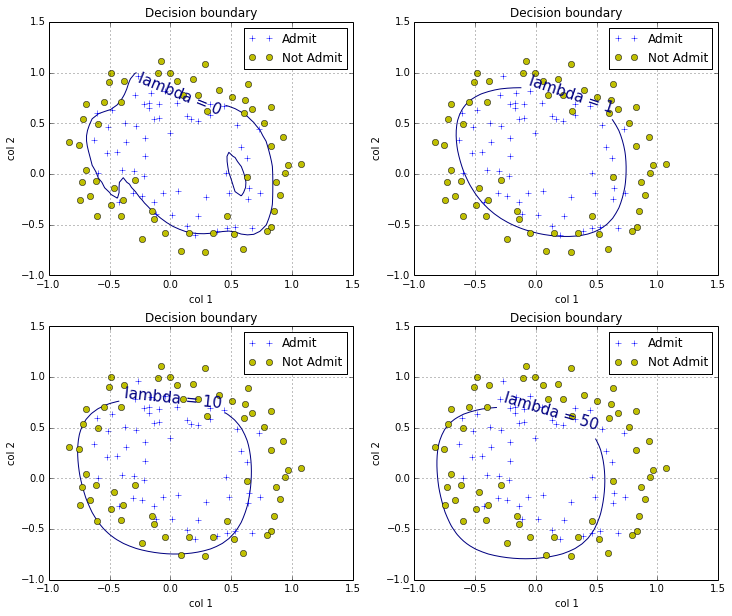
plot the boundary with different lambda
def plotMultiVariBoundary(myX, myY, mylambda=0.0):
result =optimize.minimize(costFunctionWithReg, np.zeros((mappedX.shape[1],1)), args=(mappedX,Y,mylambda), method='BFGS',
jac=gradientWithReg,options={'maxiter':500,'disp':True})
theta = result.x
minCost = result.fun
xvals = np.linspace(-1,1.5,50)
yvals = np.linspace(-1,1.5,50)
zvals = np.zeros((len(xvals),len(yvals)))
for i in xrange((len(xvals))):
for j in xrange(len(yvals)):
myfeaturesij = mapFeatures(np.array([xvals[i]]),np.array([yvals[j]]))
zvals[i][j]=np.dot(theta,myfeaturesij.T)
zvals = zvals.transpose()
u,v = np.meshgrid(xvals, yvals)
mycontour = plt.contour(xvals, yvals, zvals,[0])
myfmt = {0:'lambda = %d' % mylambda}
plt.clabel(mycontour,inline=1,fontsize=15,fmt=myfmt)
plt.title("Decision boundary")
def plotData2():
#plt.figure(figsize=(10,8)) # create a figure canvas
plt.plot(posX[:,1],posX[:,-1],'+',label='Admit')
plt.plot(negX[:,1],negX[:,-1],'yo',label='Not Admit')
plt.xlabel('col 1')
plt.ylabel('col 2')
plt.legend()
plt.grid(True)
# start to plot the data and boundary
plt.figure(figsize=(12,10))
plt.subplot(221)
plotData2()
plotMultiVariBoundary(X,Y,0.0)
plt.subplot(222)
plotData2()
plotMultiVariBoundary(X,Y,1.0)
plt.subplot(223)
plotData2()
plotMultiVariBoundary(X,Y,10.0)
plt.subplot(224)
plotData2()
plotMultiVariBoundary(X,Y,50.0)
Warning: Maximum number of iterations has been exceeded.
Current function value: 0.238242
Iterations: 500
Function evaluations: 501
Gradient evaluations: 501
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.529003
Iterations: 47
Function evaluations: 48
Gradient evaluations: 48
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.648216
Iterations: 21
Function evaluations: 22
Gradient evaluations: 22
Optimization terminated successfully.
Current function value: 0.680722
Iterations: 10
Function evaluations: 11
Gradient evaluations: 11